Florida is one of the most recognizable and visited states in the United States, known for its beaches, theme parks, warm climate, and diverse culture. But many people still ask a basic yet important question: Where is Florida State located? Understanding Florida’s geographic location helps explain its weather, economy, wildlife, history, and global importance.
This detailed article explores where Florida is located, its borders, regions, climate influence, strategic position, and why its location makes it unique among U.S. states.
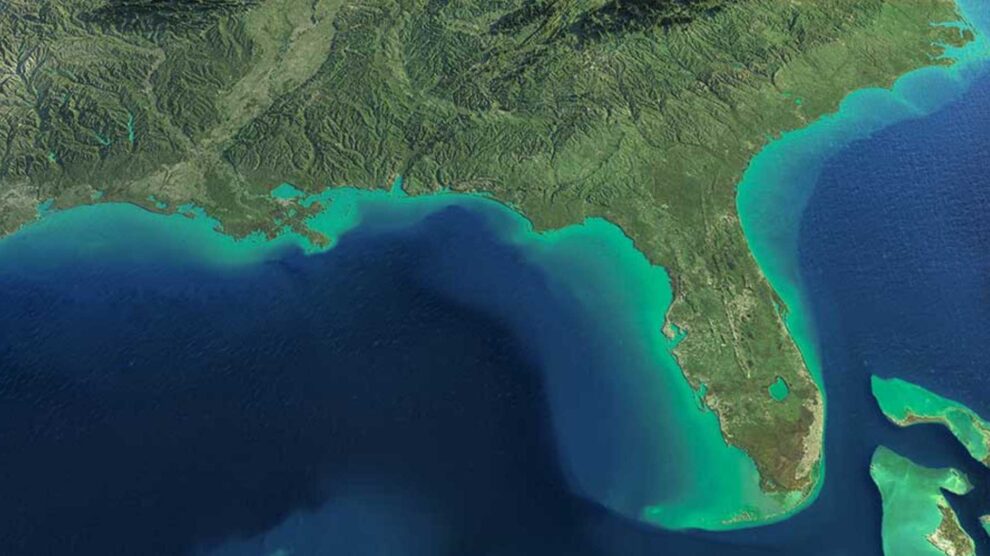
Introduction to Florida State
Florida is a state in the southeastern region of the United States. It is famous for its peninsula shape, surrounded by water on three sides, which greatly influences its lifestyle, economy, and environment. Florida is the third most populous state in the U.S., after California and Texas, and attracts millions of visitors every year from around the world.
The state’s location places it at a crossroads between North America, the Caribbean, and Latin America, making it culturally and economically significant.
Where Is Florida Located in the United States?
Florida is located in the southeastern corner of the United States. It is the southernmost state on the U.S. mainland, excluding Hawaii.
Geographic Position:
- Region: Southeastern United States
- Hemisphere: Northern Hemisphere
- Latitude: Approximately 24° to 31° North
- Longitude: Approximately 80° to 87° West
Florida extends southward from the southeastern U.S. into subtropical and tropical latitudes, which explains its warm climate throughout the year.
States That Border Florida
Florida shares land borders with only two U.S. states, both to the north:
- Georgia – Located to the north and northwest
- Alabama – Located to the northwest
Unlike most states, Florida does not share borders on all sides because it is mostly surrounded by water.
Bodies of Water Surrounding Florida
Florida is unique because it is bordered by three major bodies of water, giving it the longest coastline in the continental United States.
To the East:
- Atlantic Ocean
To the West:
- Gulf of Mexico
To the South:
- Straits of Florida, which separate Florida from Cuba
This water-surrounded geography plays a major role in Florida’s tourism, shipping, fishing, and climate.
Florida’s Shape and Physical Geography
Florida is shaped like a long peninsula extending southward from the southeastern United States. This peninsula is about 447 miles (720 km) long, making Florida one of the longest north-to-south states in the country.
Key Physical Features:
- Flat terrain with low elevation
- Extensive wetlands, including the Everglades
- Thousands of lakes and rivers
- Sandy beaches and barrier islands
Florida is also the lowest state in the U.S., with its highest point, Britton Hill, only 345 feet (105 meters) above sea level.
Major Regions of Florida
Florida can be divided into several geographic and cultural regions based on its location:
1. North Florida
- Closest to the Deep South
- More rural and traditional
- Cooler winters compared to South Florida
2. Central Florida
- Home to major cities like Orlando and Tampa
- Known for theme parks and tourism
- Mix of inland lakes and coastal areas
3. South Florida
- Includes Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and the Florida Keys
- Tropical climate
- Strong Caribbean and Latin American influence
Each region reflects how Florida’s location affects climate, culture, and economy.
Where Is Florida Located in Relation to the World?
Florida’s location makes it one of the most internationally connected U.S. states.
Nearby Countries:
- Cuba – About 90 miles south of Key West
- Bahamas – East of Florida
- Mexico – Across the Gulf of Mexico
Because of this, Florida acts as a gateway between the United States and Latin America, especially for trade, travel, and cultural exchange.
Why Florida’s Location Is Important
Florida’s location is not just a point on the map—it has shaped the state’s identity and global role.
1. Climate Influence
Florida’s southern latitude gives it:
- Warm temperatures year-round
- Mild winters
- High humidity
- Seasonal hurricanes
South Florida has a tropical climate, while North Florida has a humid subtropical climate.
2. Tourism Hub
Florida’s location near warm oceans makes it a top tourist destination:
- Beach vacations
- Cruise ship ports
- Theme parks like Disney World and Universal Studios
Millions of tourists visit Florida annually because of its easy access by air and sea.
3. Trade and Shipping
Florida’s coastal position supports:
- Major seaports (Miami, Tampa, Jacksonville)
- International trade routes
- Cruise industry leadership
The state plays a vital role in U.S. maritime commerce.
4. Wildlife and Ecosystems
Florida’s location allows for unique ecosystems:
- Coral reefs (Florida Keys)
- Mangroves
- Wetlands
- Tropical and subtropical wildlife
Many species found in Florida are not found anywhere else in the continental U.S.
Florida’s Capital and Major Cities
Capital City:
- Tallahassee
- Located in North Florida
- Chosen due to its central location between historic cities
Major Cities:
- Miami – Southeastern coast, international city
- Orlando – Central Florida, tourism capital
- Tampa – Gulf Coast, economic hub
- Jacksonville – Northeast Florida, largest city by area
Each city’s development is closely tied to Florida’s geographic location.
Florida’s Time Zone Location
Florida is located in two time zones:
- Eastern Time Zone – Most of the state
- Central Time Zone – Western Panhandle
This split reflects Florida’s wide east-to-west spread.
Conclusion
So, where is Florida State located? Florida is located in the southeastern United States, bordered by Georgia and Alabama, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and Straits of Florida, and positioned just north of the Caribbean. Its peninsula shape, coastal surroundings, and southern latitude make it one of the most geographically unique states in the country.
Florida’s location influences everything—from its climate and culture to its economy, tourism, and global connections. Whether you are studying geography, planning travel, or writing an academic article, understanding where Florida is located provides valuable insight into why the state is so important and distinctive.